In the world of floating infrastructure, stability is everything.
Whether it’s a floating jetty, solar plant, or modular event platform, the strength and safety of any floating system ultimately depend on how well it is moored. Mooring systems — the anchor and tether mechanisms that keep floating structures in place — are the silent backbone of every successful floating installation.
In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of mooring systems used in floating infrastructure projects, when and where they are applied, and how to choose the right one based on site conditions and use cases.
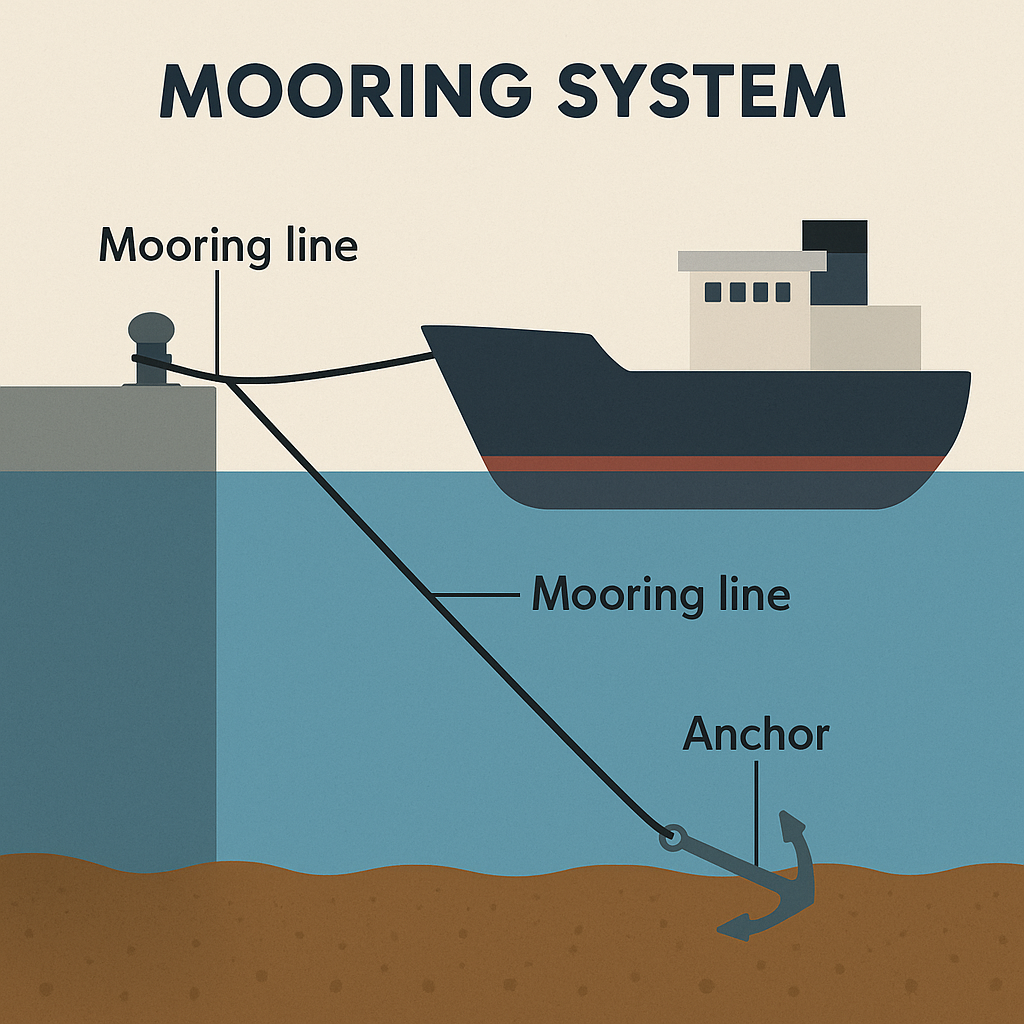
Floating infrastructure is constantly at the mercy of natural forces — wind, waves, currents, and water level fluctuations. A poorly moored system can drift, tilt, or even capsize, leading to costly damage or operational downtime.
A well-engineered mooring layout:
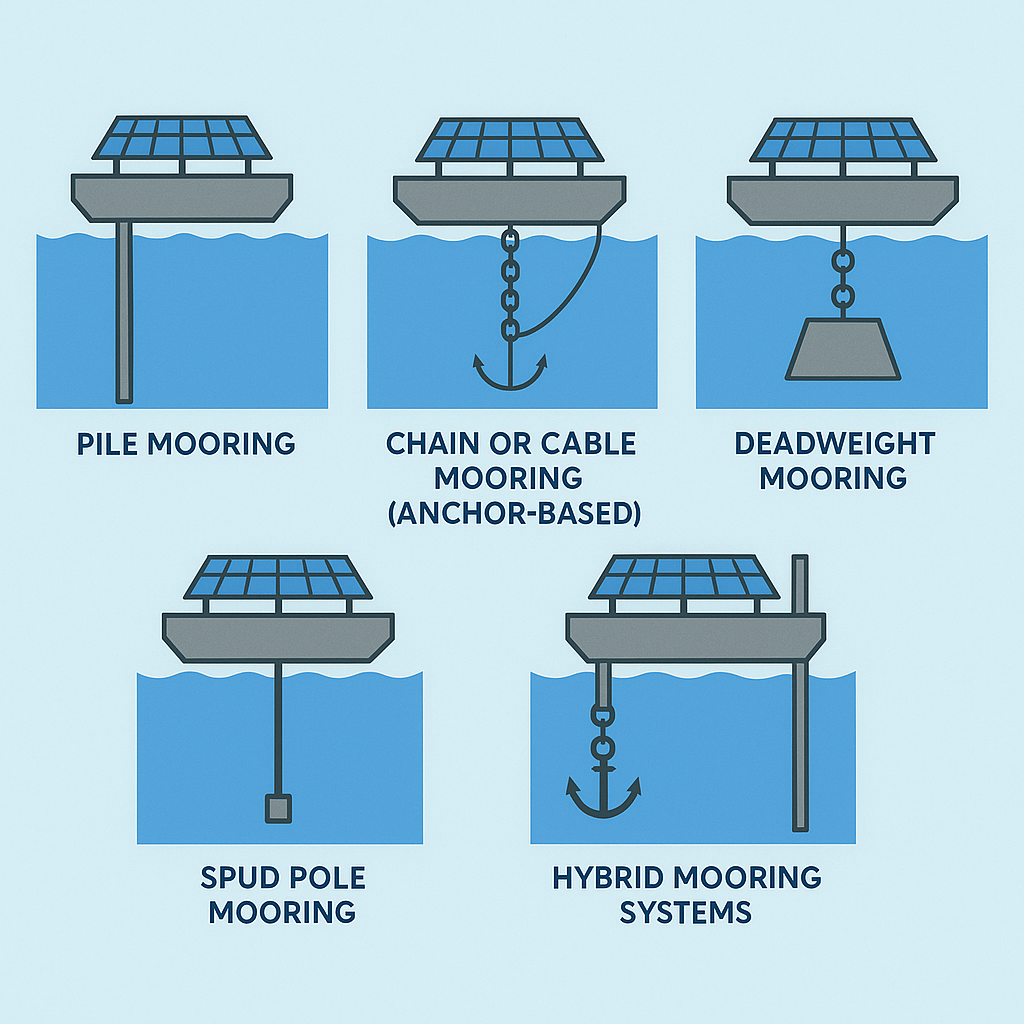
Floating infrastructure commonly uses a mix of the following mooring systems, depending on waterbody type (river, lake, coastal), project scale, and operational requirements.
What It Is:
Vertical steel or concrete piles are driven into the waterbed, and the floating structure slides up and down along these piles with water level changes.
Best For:
Advantages:
Limitations:
What It Is:
Heavy-duty chains or steel cables connect the floating structure to anchors or deadweights laid on the waterbed.
Best For:
Advantages:
Limitations:
What It Is:
Massive concrete blocks (deadweights) hold the floating structure in place via tensioned cables or ropes.
Best For:
Advantages:
Limitations:
What It Is:
Removable vertical poles (spuds) are inserted through sleeves in the floating platform and anchored into the riverbed or lakebed.
Best For:
Advantages:
Limitations:
What It Is:
A combination of two or more mooring types — such as pile + chain, or deadweight + spud — depending on project needs.
Best For:
Advantages:
Limitations:
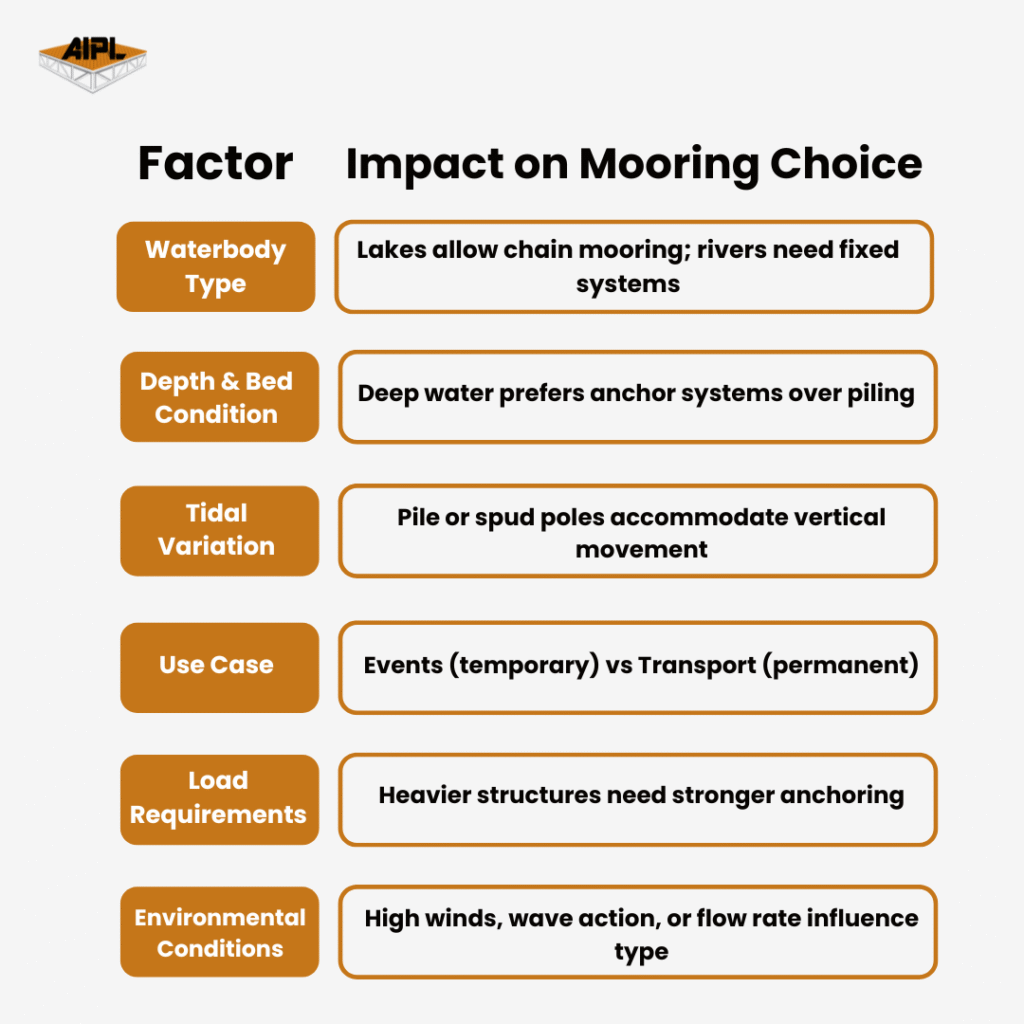
Choosing the right mooring layout isn’t just about anchoring the platform — it’s about ensuring long-term performance.
Here are key factors AIPL engineers consider:
Every floating project begins with a solid foundation — and in water, that foundation is your mooring system.
At AIPL, we engineer custom mooring layouts that consider not just technical viability but also environmental impact, operational goals, and future scalability. Whether it’s a floating jetty, solar plant, or modular barge, our design-first approach ensures that your infrastructure stays safe, stable, and functional — year after year.
🔗 Got a project in mind?
Let’s talk about the right mooring solution for your waterbody.
Contact AIPL for a custom mooring layout consultation.
1. What is AIPL’s Acquaworks – Construction Pontoon Series?
Acquaworks is a modular heavy-duty pontoon system designed to convert any waterbody into a safe, stable, and high-performance worksite for cranes, excavators, dredgers, and piling rigs.
2. What makes Acquaworks suitable for heavy-duty marine construction?
It features reinforced interlocking decks, spud wells, winch anchoring, non-slip surfaces, guardrails, and safe crew access.
3. What types of construction operations can be performed?
- Acquaworks Lift – Crane Operations
- Acquaworks Dig/Dredge – Excavation & Dredging
- Acquaworks Pile/Drill – Piling & Drilling
4. What are the typical platform dimensions of AIPL’s construction pontoons?
Length: 18–30 m, Width: 9–15 m, Depth: 1.2–1.8 m
5. What is the deck load capacity of AIPL’s construction pontoons?
6–8 t/m² across all models.
6. What machine loads can be sustained by AIPL’s construction pontoons?
- Lift: up to 60 tons
- Dig/Dredge: up to 45 tons
- Pile/Drill: up to 50 tons
7. Are spud systems available at AIPL’s construction pontoons?
Yes, spud wells/spud-assisted systems are available in all models.
8. What accessories can be integrated in AIPL’s construction pontoons?
Bollards, winches, guardrails, fenders, gensets, fire extinguishers, propulsion units.
9. What is Acquaworks Lift used for?
Heavy-duty floating crane operations with reinforced deck grillage and wear plates.
10. How does Acquaworks Lift ensure safety?
By using spud anchoring, wear plates, wide access zones, and predictable radius management.
11. What is Acquaworks Dig/Dredge used for?
Water-based excavation and dredging using excavators, suction heads, and slurry pumps.
12. Does Dig/Dredge support environmental compliance?
Yes, it supports silt curtains and debris screens.
13. What is Acquaworks Pile/Drill used for?
Marine piling and drilling with vibro hammers, impact hammers, and rotary rigs.
14. How does Pile/Drill maintain alignment?
Through integrated reaction points, tie-downs, and guide posts.
15. Is Acquaworks easy to transport and install?
Yes, it is modular, transport-friendly, and quick to reconfigure.
16. How is crew safety ensured?
Non-slip decks, guardrails, wide access zones, and organized utilities.
17. Can pontoons be reconfigured?
Yes, they can be adapted for lifting, dredging, or piling operations.
18. What makes Acquaworks better than traditional barges?
Modularity, predictable stability, quick assembly, better safety, and integrated utilities.
19. How is deck organization maintained?
Through integrated trays, clamps, and dedicated utility routes.
20. Can propulsion be added?
Yes, propulsion units can be integrated for maneuvering.