In the evolving world of marine and river-based infrastructure, industrial barges play a pivotal role in enabling large-scale logistics, offshore construction, and energy projects. From transporting heavy cargo to serving as floating work platforms, barges are the unsung heroes of industrial maritime operations.
As India expands its coastal and inland waterway networks under initiatives like Sagarmala and Maritime India Vision 2030, the demand for modular, efficient, and customizable barge systems has seen an exponential rise. This guide dives deep into how industrial barge systems are selected, designed, and deployed for logistics and construction projects across India.
A barge is a flat-bottomed vessel designed primarily for transporting heavy or bulky goods over rivers, canals, and coastal waters. Unlike traditional ships, barges are often non-self-propelled, meaning they rely on tugboats or pushers for movement. This makes them ideal for inland water transport, construction, dredging, and marine infrastructure projects.
In India, barges have become central to major projects such as the Namami Gange river cleaning initiative, port expansion at Kandla and Paradip, and offshore construction works near Mumbai and Kochi. The rise of modular barge designs has further revolutionized the sector by allowing flexible configurations for different industrial purposes.
Choosing the right barge depends on the nature of the project, type of cargo, and operational environment. Each application demands a specific design, material, and configuration.
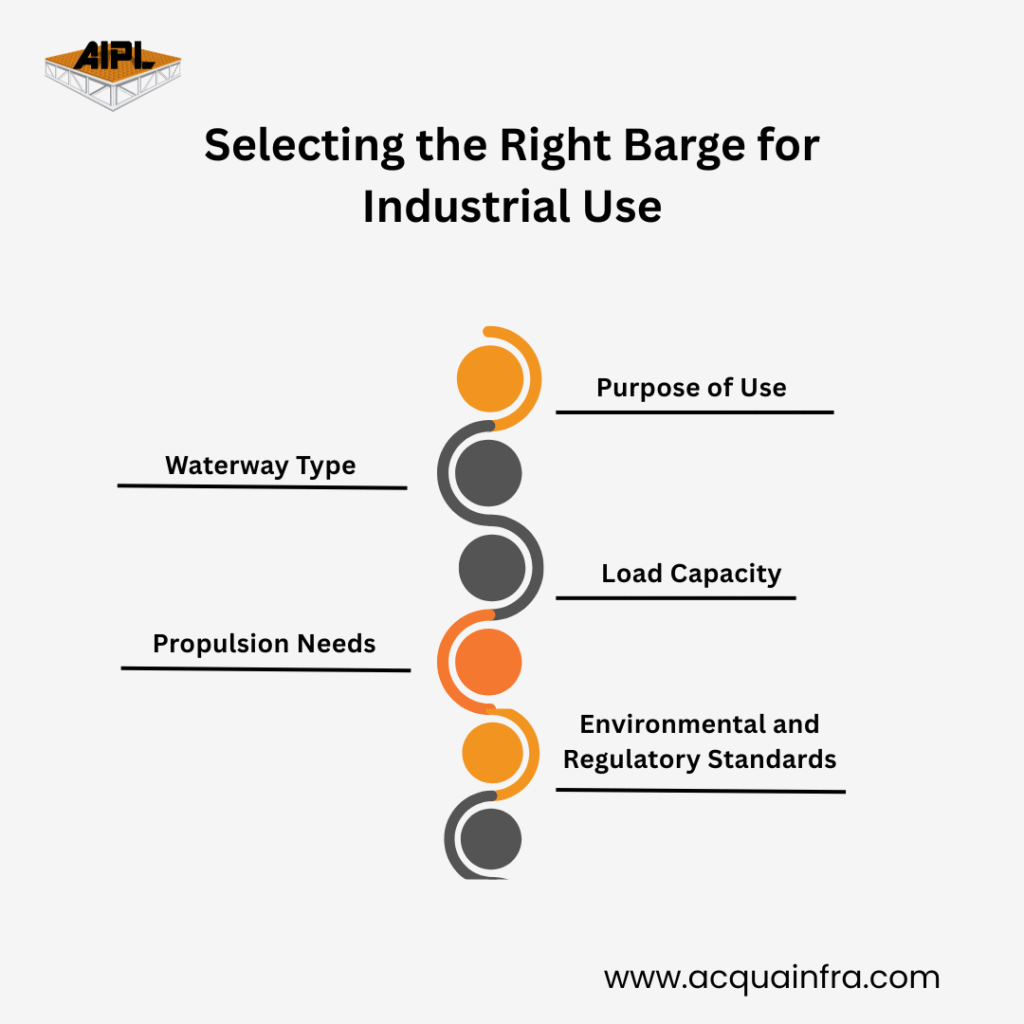
Key factors influencing selection include:
In recent years, Acqua Infra and other Indian manufacturers have focused on creating customizable modular barge systems that can be easily transported, assembled, and adapted to different project requirements — significantly reducing lead time and operational costs.
Industrial barges are transforming logistics by offering a cost-efficient, environmentally sustainable alternative to road and rail transport. India’s vast network of inland waterways — such as National Waterway 1 (Ganga) and National Waterway 2 (Brahmaputra) — is being leveraged for moving heavy industrial goods, construction materials, and bulk commodities.
Advantages of using barges for logistics include:
For example, the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) has successfully facilitated cargo transport between Haldia, Varanasi, and Patna using industrial barge fleets — showcasing how inland logistics is evolving as part of India’s blue economy vision.
Beyond transportation, barges also serve as floating construction platforms for infrastructure development, especially in offshore and riverine environments.
These construction barges provide stable and safe bases for cranes, piling rigs, and heavy equipment used in:
Design considerations for construction barges include:
In India, the Modular Floating Pump Pontoon at Hirakud Reservoir and floating piling barges used in coastal port works are prime examples of how modular barge systems are being customized for construction efficiency.
Modern industrial barge systems are designed for durability, adaptability, and reduced environmental impact.
Material advancements include:
Digital design tools and modular fabrication have further allowed manufacturers to produce barges that are easier to transport, assemble, and maintain, cutting project timelines significantly.
Sustainability has become a driving factor in marine operations. Barges, by nature, consume less fuel per ton-kilometer and have a lower carbon footprint than trucks or trains.
Modern barge systems are now being integrated with:
This aligns perfectly with India’s National Green Port Policy and the global shift toward sustainable marine logistics.
India’s vision of becoming a global logistics powerhouse is inseparable from the growth of its inland and coastal waterway networks. With ongoing projects in Varanasi, Guwahati, Kochi, and Paradip, the role of industrial barge systems will continue to expand — from transporting goods to powering offshore infrastructure.
The integration of AI-driven navigation, modular automation, and eco-efficient materials will define the next generation of barges — making them smarter, cleaner, and more capable.
As modular marine engineering evolves, barges will remain the backbone of India’s floating logistics and construction ecosystem, connecting industry, innovation, and sustainability across its vast waterways.
Ready to modernize your maritime or inland waterway project? Contact Acquafront Infrastructure today for a custom modular barge solution!
It transports heavy cargo and serves as a floating work platform for construction and dredging projects in waterways.
They allow for flexible configurations, easy transport/assembly, and significantly reduce operational lead time and cost.
Barges move high volumes of cargo at lower costs and possess a lower carbon footprint per ton-kilometer than trucks or trains.
The selection depends on the project's purpose, the waterway type, the required load capacity, and compliance with IRS regulatory standards.
They provide a stable base on the water for mounting heavy machinery like cranes and piling rigs for bridge and port construction.