
India is undergoing a massive energy transformation. With the ambitious target to achieve 500 GW of renewable energy by 2030, solar power has emerged as one of the cornerstones of this mission. But with increasing land scarcity, environmental challenges, and a growing thirst for clean energy, India is now exploring innovative ways to harvest solar power — not just from land, but also from water bodies.
Floating Solar Plants and Land-Based Solar Parks have become two primary options for large-scale solar power generation. But which of these is more efficient? And more importantly, which one is better suited for India’s diverse geography and infrastructural needs?
Let’s dive into the details.
Floating Solar Plants, also known as floatovoltaics, are solar power systems installed on the surface of calm water bodies such as lakes, dams, reservoirs, and even abandoned mining pits.
Bonus Benefit: They utilize underused water surfaces while preserving valuable land for agriculture, forestry, or urban development.
Land-Based Solar Parks are the conventional large-scale solar farms most people are familiar with — large, open fields covered with rows of solar panels.
Challenge: They require vast stretches of flat land, which in land-scarce countries like India can lead to conflicts with agricultural, residential, or ecological land use.
| Criteria | Floating Solar Plants | Land-Based Solar Parks |
| Land Usage | No land required | Requires large tracts of land |
| Cooling & Efficiency | 5–15% higher due to natural water cooling | Lower due to heat buildup |
| Installation Cost | 20–30% higher initially | Lower |
| Maintenance | Easier (less dust, algae control) | Frequent cleaning, higher manpower |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces evaporation, minimal land disturbance | Land clearing, possible soil degradation |
| Scalability | Limited to available water bodies | Easier in desert or barren lands |
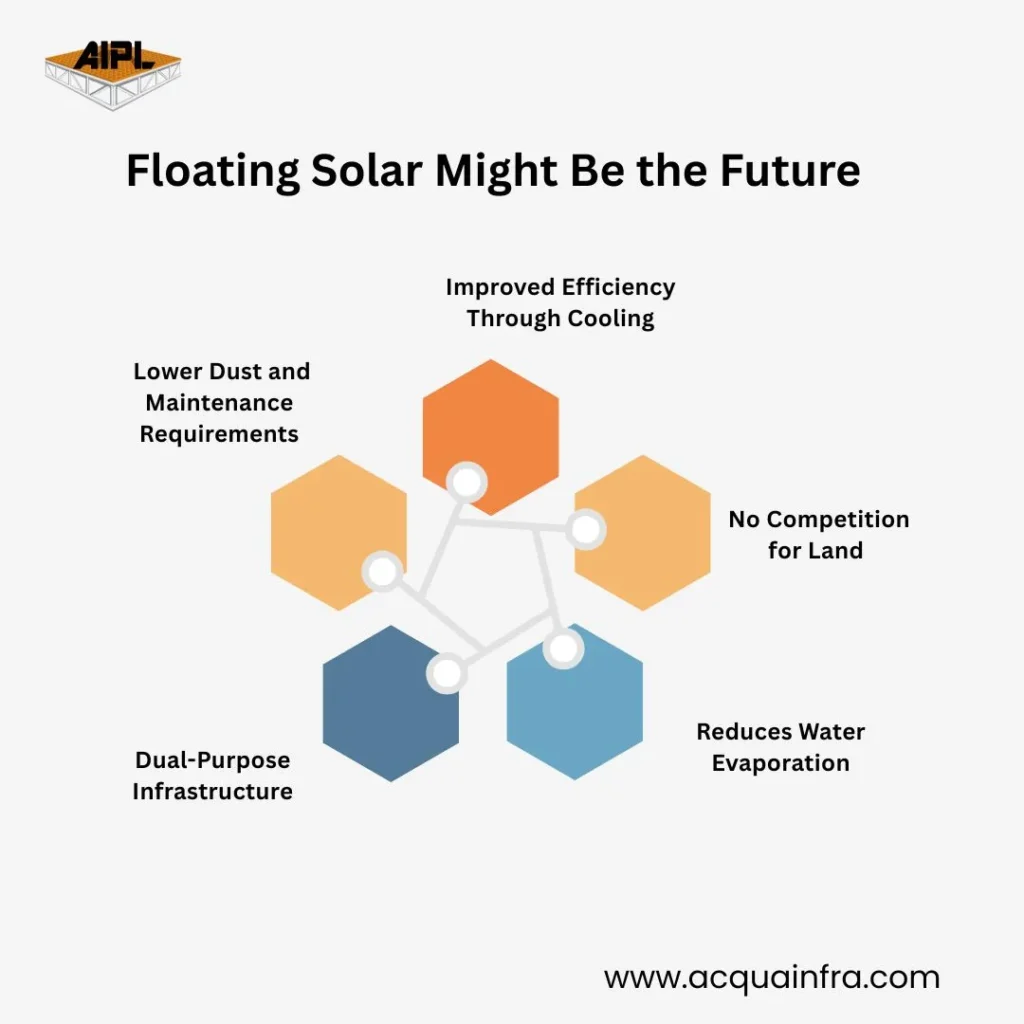
As someone working closely in the maritime and floating infrastructure space, I’ve observed how water bodies are emerging as an untapped asset for renewable energy. Here’s why floating solar is not just a trend — it’s a logical next step.
Solar panels tend to lose efficiency as they heat up, especially in India’s tropical climate. Floating them over water allows the panels to remain cooler, improving their performance by 5–15% compared to land-based systems. This natural cooling effect translates into better energy yields and longer panel life.
Land is scarce, especially in densely populated or agriculturally fertile regions. Floating solar plants sidestep this issue by utilizing idle water surfaces like reservoirs, lakes, and even industrial ponds. This allows land to be preserved for food production, forestry, or urban development.
A lesser-known but valuable benefit is that floating solar panels can significantly reduce evaporation rates in reservoirs and dams — particularly useful in water-stressed regions. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), covering just 10% of a water body’s surface can reduce evaporation by up to 70%.
In regions where water reservoirs exist primarily for drinking water or irrigation, adding solar panels on their surface transforms them into dual-purpose utilities — generating clean energy while conserving water.
Since floating panels are away from dust-laden environments like fields or roads, they require less frequent cleaning. Algae growth on water can also be managed naturally or with occasional cleaning, reducing operational expenses.
While floating solar has clear advantages, land-based solar parks continue to play a crucial role, particularly in:
When vast stretches of inexpensive, barren, or desert land are available (like in Rajasthan or Gujarat), land-based solar parks offer the most scalable option for adding gigawatt-scale capacities.
Land-based solar parks are easier to connect to the grid, especially in industrial zones or areas with established transmission lines. This reduces infrastructure costs and delays.
Setting up and servicing land-based solar systems is logistically easier than deploying maintenance teams over water, making them preferable for rapid, large-scale rollouts.
India is witnessing a growing number of floating solar projects, driven by state governments and private firms:
This was one of India’s first floating solar plants, installed on the Banasura Sagar reservoir in Wayanad. Although small in size (500 kWp), it demonstrated the technical feasibility of such systems in Indian conditions.
Currently India’s largest floating solar installation, this 100 MW project by NTPC covers a portion of the Ramagundam reservoir and significantly reduces water evaporation while powering nearby areas.
These examples indicate the growing acceptance and adaptability of floating solar infrastructure in India’s energy mix.
As the demand for floating solar infrastructure grows across India, the importance of having experienced, technically sound, and dependable partners becomes crucial. This is where AIPL (Acquafront Infrastructure Pvt. Ltd.) plays a pioneering role.
We at AIPL specialize in delivering integrated, turn-key solutions for floating infrastructure projects — from concept design to commissioning.
On-Ground Execution & Maintenance Support: From procurement to installation and post-project maintenance, AIPL ensures seamless project management, helping clients maximize ROI and system uptime.
In pure numbers, floating solar plants outperform land-based parks by around 5–15% in efficiency, thanks to natural cooling and reduced dust interference.
However, each has its place:
The future of India’s solar story lies in a hybrid approach — combining the vast potential of open lands with the underutilized promise of its water bodies.
Yes — upfront costs can be 20–30% higher due to floating platforms and anchoring systems. However, higher efficiency and operational savings balance the difference over time.
Modern floating platforms are engineered to withstand high winds, heavy rains, and fluctuating water levels. Designs follow international maritime safety standards.
Studies show that covering 20–30% of a water body’s surface can reduce evaporation by 50–70% — a game-changer in water-scarce areas.
Properly designed systems allow sunlight penetration and oxygen circulation, minimizing ecological disruption. Some projects have even improved water quality by reducing algae growth.
Contact us today for customized floating solutions that guarantee performance, durability, and peace of mind.